HOISTED FROM THE ARCHIVES: High Patriarchy
Hoisting and breaking this out so I will be able to find this easily in the future. Originally at <https://braddelong.substack.com/p/high-patriarchy>…
Tian Chen Zeng, Alan J. Aw, & Marcus W. Feldman: Cultural Hitchhiking & Competition Between Patrilineal Kin Groups Explain the Post-Neolithic Y-Chromosome Bottleneck <https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-04375-6.pdf>;
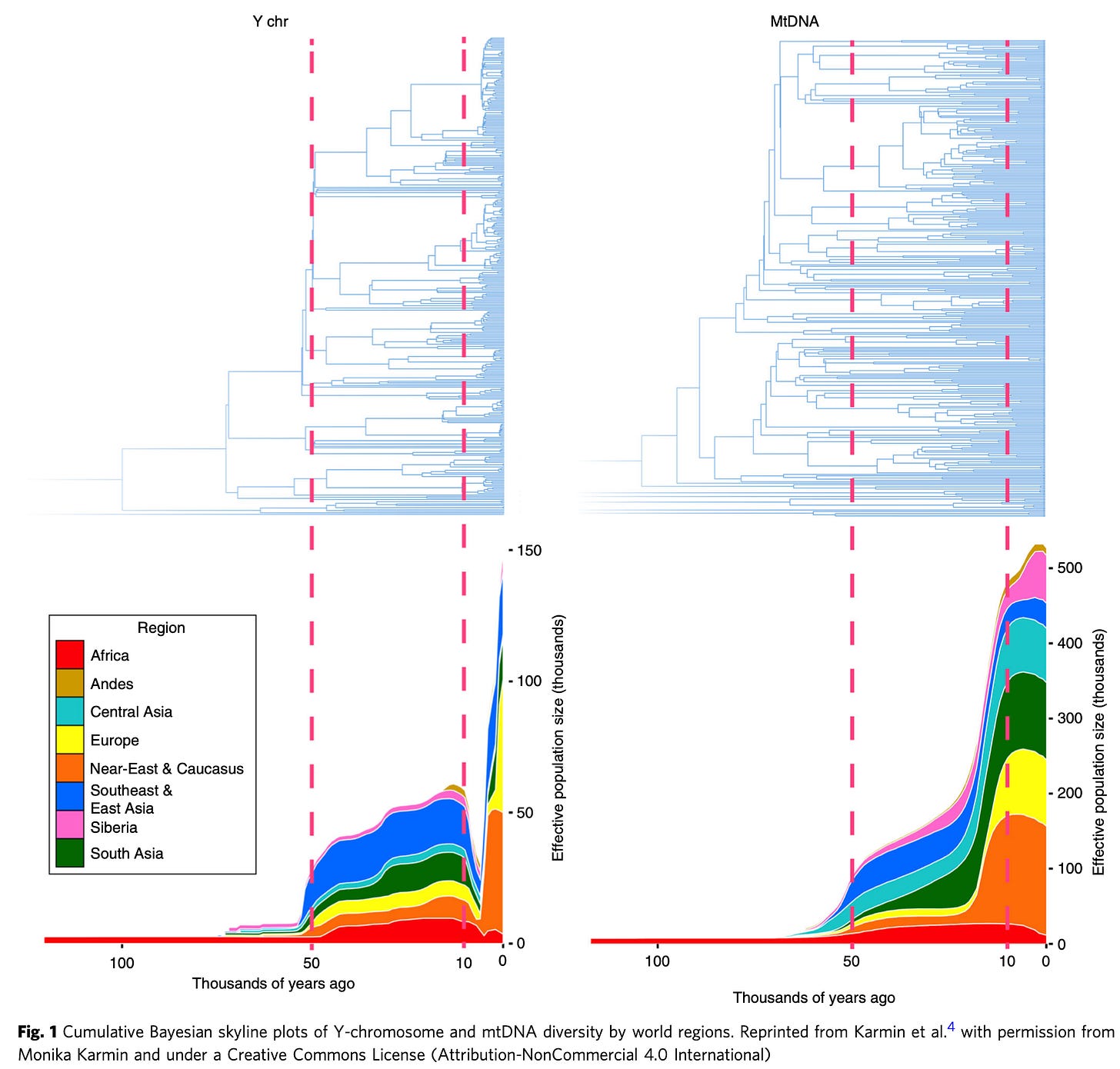
M. Karmin & al. (2015): A Recent Bottleneck of Y Chromosome Diversity Coincides with a Global Change In Culture (Genome Res. 25, 459–466) <https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25770088/>:
All of us (men) have y-chromosomes that are those of Y-Chromosome Adam back roughly some 200,000 years ago, with whatever mutations of that have occurred since. Looking at the ensemble of y-chromosomes allows us to construct a tree by virtue of which y-chromosomes differ by one base pair, which by two, and so on. The amount of branching at each calculated date in the past tells us what the effective population size (of men) was then, for each y-sperm that fertilizes an egg is another chance for mutations to occur.
Similarly, all of us have mitochondria that are those of Mitochondrial Eve, back some back roughly some 200,000 years ago, with whatever mutations of that have occurred since. Looking at the ensemble of mitochondria allows us to construct a tree by virtue of which mitochondria differ by one base pair, which by two, and so on. The amount of branching at each calculated date in the past tells us what the effective population size (of men) was then, for each fertilized egg is another chance for mitochondrial mutations to occur.
Note that between out-of-Africa and the coming of agriculture—between 50 and 10 thousand years ago—the effective male population size was 30,000 at the start and 60,000 at the end of that late-Mesolithic Age: 30,000 and 60,000 of the men alive back then have living descendants today. By contrast, the effective female population size was more like 100,000 50 thousand years ago and more like 450,000 10 thousand years ago.
But then, with the invention of agriculture, things go bonkers. Mitochondrial lines continue to multiply at a furious pace as mutations happen. Y-chromosome lines… sharply slow down in their multiplication, as the men’s side of the effective population crashes. At the trough, 5 thousand years ago, the men who have living descendants today amount to only 1/20 as large a fraction as the fraction of women alive then who have living descendants today.
This would seem to mean that -8000 to 1 saw substantial polygyny for a few men, and non-reproduction for others. It also means the inheritance of male reproductive advantage: that if your great-grandfather had the resources to have more than one wife, the odds were higher that you were at the top of the inequality pyramid and had the resources to have more than one wife as well. Patriarchal reproductive inequality was in that age both substantial and inherited.
This is polygyny: one man, many wives—and lots of men with no wives and little sexual access to women. This is the Biblical Patriarch Jacob: 13 children with two wives and two concubines. Jacob and Leah’s children were Reuben, Simeon, Levi, Judah, Issachar, Zebulun, and Dina; Jacob and Rachel’s children were Joseph and Benjamin; Jacob and Zilpah’s children were Gad and Asher, and Jacob and Bilhah’s children were Dan and Naphtali. And somewhere in the neighborhood there were three men—unnamed, possibly dead—who were without wives, and without children.
Leah, Rachel, Zilpah, and Bilhah’s mitochondrial DNA lineages were passed down. The three nameless men’s y-chromosome lineages were not: only Jacob’s was.
Maintaining polygyny for a number of generations requires great social pressure and great societal inequality among men. It also requires a great deal of subservience among women. Back then, women were, to a substantial degree, property: the property of their fathers, and then of those in the patriarchal polygynous network who gained control over them. And back then, a great many men were without resources‚ for the overwhelming majority of men would, if they had resources to deploy to attain any form of social power, would have chosen to use those resources to marry. And yet many of them could not do so. How much social power had to be deployed against them, and in what form, to enforce their non-marrying?
This age of super-patriarchy stands out in our genetic record. The social structures and institutions to support it are not there before -8000 and do not persist since the year 1.
What was human life and human inequality like back in this patriarchal age? What brought it on? What made it come to an end?
And what was life like for women in those years—because making women share husbands is something that requires a lot of social power deployed and exerted to enforce?
References:
DeLong, J. Bradford. 2025. “HOISTED FROM THE ARCHIVES: High Patriarchy”. DeLong’s Grasping Reality. October 22. <>.
DeLong, J. Bradford. 2021. “High Patriarchy, & BRIEFLY NOTED: For 2021-12-31 Fr”. DeLong’s Grasping Reality. December 31. <https://braddelong.substack.com/p/high-patriarchy>.
Karmin. M. & al. 2015. A Recent Bottleneck of Y Chromosome Diversity Coincides with a Global Change In Culture (Genome Res. 25, 459–466) <https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25770088/>:
Zeng, Tian Chen, Alan J. Aw, & Marcus W. Feldman: Cultural Hitchhiking & Competition Between Patrilineal Kin Groups Explain the Post-Neolithic Y-Chromosome Bottleneck <https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-04375-6.pdf>;